Process
"Hogging" is a process similar to sawing. With it, a clean cutting surface should be generated and the separated trimmings should be subsequently shredded into shavings for feeding to the extraction system.
Applications
- Hoggers are frequently used on double end tenoners for formatting the workpiece.
- With industrial edgebanders hoggers are used in the sizing unit.
- In multiblade saws for removing remaining pieces of differing widths, which arise opposite the stop.
Technical method
- With "half and half systems", also known as "double hogging units", the operator works with two tools operating in the down-cut . Each individual hogger is responsible for around half of the hogging (from top/from bottom). However, with transversal processing on edgebanders there is a risk that the previously glued lengthwise edge may be torn off. A protection milling unit is therefore used here. This is located before the hoggers and mills in the up-cut, a few centimetres from the front edge of the workpiece, somewhat deeper than the hogger. Once the edge has been glued on, the small offset of approx. 0.2 to 0.5 mm is barely perceptible. This aggregate is often referred to by manufacturers as a protection milling unit.
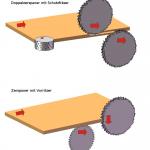
- With the "pinion hogger" a scoring saw is used before the hogger (see also scoring aggregate, similar to with the sliding table saws.
- Less common is a technical method whereby a splinter guard is used, which is positioned precisely on the contour of the hogger and prevents the tearing off of material during processing (in a similar way to counter battens).