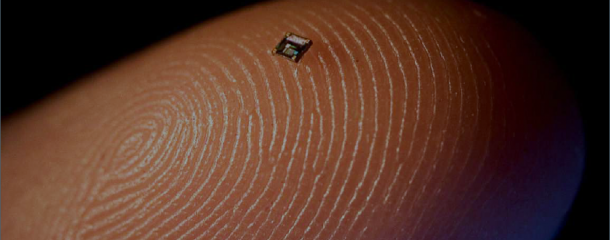
RFIDRFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identification and is a system for automatic and non-contact identification and localization using microchips. It consists of a transponder (microchip without a separate power source), which is located on the object to be identified, and a reader. The transponder contains an identifying code, by which the reader can identify it using high-frequency electromagnetic waves. For the meaningful application of RFID systems, for example in industry, an appropriate software for managing and processing the data is usually necessary. Origin and developmentAlready in World War II, systems for distinguishing between friend and enemy using the reflection of radar waves were used in tanks and planes. This first industrial application was a development of the Siemens Group in the 1960s for identifying rail cars and car parts. In the 1970s, RFID systems were used in larger numbers for the first time, e.g. for retail security. Only in the 1980s, the RFID technology became used as an inexpensive mass-produced good, i.a. through support programs of various states. Since then, it has been used, for example, in toll systems, electronic locks, for cashless vending, in ski passes, electronic immobilizers and others. At this point, the first attempts were also made to use it in the furniture industry. However, because of the much more expensive hardware, the system could not prevail against the barcode workpiece identification. Since the 2000s, however, due to the significantly lower costs and the greater general circulation, these systems have been used more often, e.g. with the RFID.System developed by IMA. A major advantage of the RFID technology, compared to barcode systems, is that the workpiece surface is not affected. Since some of the now used microchips are no more expensive than barcode labels, they can also remain on the workpiece, while barcode labels usually have to be removed before delivery. In 1993, the company Leitz introduced the TIM (Tool Information Management system, which allows for the automatic identification of tools on CNC machining centers. |
CNC machining centres, robots894
Edgebanding, edge processing627
Saws, cutting machines436
Planers, 4-sided moulders186
Routers, shapers, tenoners, profilers181
Drilling, mortising machines134
Presses, clamps, joining machines201
Sanding machines320
Mechanisation, storage, packing technology199
Surface coating152
Production lines127
Heating, drying, waste chopping63
Dust extraction, compressed air, vacuum140
Assembly, worktables15
Lathes29
Tools, sharpening technology91
Equipment, Other machines131