PostformingTechnical term for the subsequent (post-) shaping (forming) of an already applicated surface material on panel workpieces along the edge profile. This method was firstly introduced in 1976 through the German company IMA Klessmann GmbH. The surface material is applied to the panel workpiece in a way that it overlapse over a profiled edge. In a secondary working process on a postforming machine the material is applied (stroke and classical throughfeed method). Postformingparts are used where woodbased materials and there edges are not so appropiate of moisture, chemicals and mechanical stress.
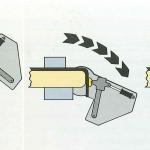
Postforming methodStroke methodThe starting material is a panel sheet which has a profiled edge and the surface with another material glued on it.
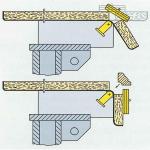
Inner curves occur where work topes need to be fitted to a wall. Such worktop ends where they are connected to a wall are especially endangered, and thats why the postforming process is especially relevant for such applications, because as a result of the postforming process there is a continuously coded layer. In this case the heating rail does not circle around the profile, but the workpiece is put around the heating rail and the gap between the two worktop pieces is filled with a accurate batten (see picture). Manufacturers of Postforming machines stroke method (as of 2010): Throughfeed methodThe starting material has a coated surface and pre-profiled edges. The machine concept is from its main structure like an edgebander. The main difference is a pressure zone. Such throughfeed postforming machines have a pressure zone consisting of many rubber rollers which can be adapted exactly to the workpiece profile in there inclination. For the setup of the machine a preprofiled sheet is put in the machine. The rollers of the pressure zone are a line to the edge profile in such a way, that the overlapping surface material, starting from the surface of a panel, is folded around the profile. Radiant heaters and heating fans ensure that the necessary temperature for the forming process is reached. Some machines feature an automatic glue application station, other machines require a manual application of the glue. Depending of the configuration the following aggregates are a flush trimming aggregate (see flush/radius/chamfer milling units) for the flush trimming of the glued surface material. Further aggregates for special processings could follow. High performance machines process those the workpiece and the postforming segment even before the gluing to size so that the joint is not visible anymore. Manufacturers of postforming machines for the throughfeed method up to 25 m / min (As of 2010): The following surface materials can be formed in the stroke method and in the throughfeed method:
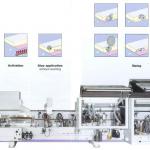
Direct PostformingIn the direct postforming method the starting material consists of unprofiled, coated panels without an overlapping of the surface material. The machine does a profiling of the forming zone by itsself and uncovers as much of the coating material as is needed for the coating of the edge (see picture). In the following step the overlap is folded around the edge profile, as described in the throughfeed process. Advantages of the direct method:
Possible surface materials:
Manufacturers of machines for direct postforming in a throughfeed method up to 20 m / min (as 2010)
Postforming glues
Alternative terms, related terms
|
CNC machining centres, robots894
Edgebanding, edge processing627
Saws, cutting machines436
Planers, 4-sided moulders186
Routers, shapers, tenoners, profilers181
Drilling, mortising machines134
Presses, clamps, joining machines201
Sanding machines320
Mechanisation, storage, packing technology199
Surface coating152
Production lines127
Heating, drying, waste chopping63
Dust extraction, compressed air, vacuum140
Assembly, worktables15
Lathes29
Tools, sharpening technology91
Equipment, Other machines131