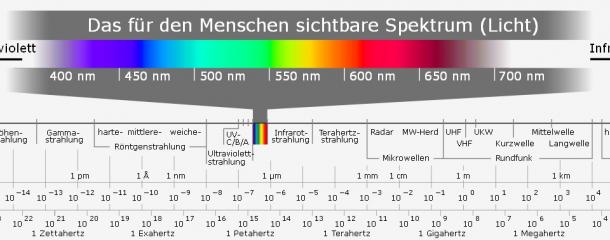
IR radiationThe frequency of the infrared radiation (IR radiation) lies between 300 GHz and around 400 THz below visible light. The wavelength of the IR radiation lies above visible light, between 1 mm and 780 nm. (see illustration 1) The applications of IR radiation in industry are widely diverse. It is possible to dry or harden materials, soften and deform plastics. Infrared lasers are used for welding, labelling and cutting materials. The property of IR radiation is used here, whereby heat is transferred without a contact medium. Only upon contact with the material are the electromagnetic rays converted into heat. A further application is the heating of working areas. These are commonly referred to as cold lamps or dark radiators. Infrared radiation possesses a heat transfer capacity many times greater than that of convection (heat flow). A further advantage of IR radiation lies in the fact that the radiation sources can be activated and deactivated within just a short time, which has a positive effect on the energy consumption of the heating / drying process. In the field of wood processing - in particular with surface coating - the use of infrared radiation is frequently found in the applications:
Combinations of IR drying and hot-air drying are common for example. |
CNC machining centres, robots895
Edgebanding, edge processing632
Saws, cutting machines437
Planers, 4-sided moulders188
Routers, shapers, tenoners, profilers181
Drilling, mortising machines135
Presses, clamps, joining machines201
Sanding machines323
Mechanisation, storage, packing technology202
Surface coating152
Production lines127
Heating, drying, waste chopping62
Dust extraction, compressed air, vacuum135
Assembly, worktables15
Lathes29
Tools, sharpening technology91
Equipment, Other machines132